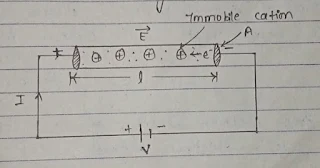
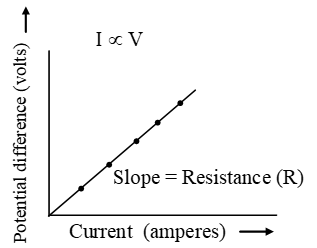
Its unit is ohm
Wednesday, May 26, 2021
DC Circuit
Saturday, May 22, 2021
Class 10 Science (1Marks) Physics
This test is strictly based on the curriculum of SEE science class 10 for one marks questions. Your feedbacks are heartily welcome.
Science Practice Exam 10
Thursday, May 20, 2021
Monday, May 17, 2021
Question Electricity and magnetism
d) What type of combination of cells is shown in the given circuit? Calculate the power of the bulb if 0.2Acurrent flows through the curcuit.![]()
Answer the following questions:
a) What is ment by one kilowatt hour in electricity?
Ans: The electricity consumed by electric load of load of one kilowatt power in one hour is known as one kilowatt hour in electricity.
b) What is meant by electric current?
Ans: The flow of electron in a conducting wire is known as electric current.
c) What is meant by electric circuit?
Ans: The pathway of electricity containing combination of source, load and switch is known as electricity circuit.
d) What is meant by electricity consumption?
Ans: The amount of electricity which id converted to the other forms of energy by using load is known as electricity consumption.
e) How is electricity consumption calcutated?
Ans: To claculate the electricity consumption the product of the number of load, power, and time is calculated:
Electricity consumption= P×N×T
f) What is meant by electric power?
Ans: The amount of electric of energy consumd by a load in one second is known as electric power.
g) Which instrument is used to measure the electrical power consumption?
Ans: Meter box is used to measure the electrical power consumption. It measures the power consumption in kilowatt hour.
h) What is meant by galvanometer?
Ans: The electrical device which is used to measure small signals of current is known as galvanometer.
i) On which principle generator and dynamo depends?
Ans: The working principle of generator and dynamo depends on the principle of electromagnetic induction.
j) What are the types of generator?
Ans: Following are the types of generator:
i. AC generator
ii. DC generator, etc.
Give reasons:
a) The efficiency of a transformer is never 100%, why?
Ans: There is resistance in the coil of a transformer, so the efficiency of a transformer is never 100%.
b) Soft iron armature is used in electric bell, why?
Ans: The more the metal is soft the strength of magnet formed is more. So, soft iron armature is used in electric bell.
c) Filament lamp is filled with inert gases. Why?
Ans: In high temperature i.e. around 2900°C tungsten filament can get oxidised due to reaction with oxygen. So, to prevent oxidation and maintain the pressure, innert gas is filled in filament lamp.
d) Why is Nichrome used in heater?
Ans: Nichrome has high resistance and does not get oxidised even in high temperature like 900°C and can easily converts electric energy into heat energy. So, nichromee is used in heater.
e) Why should the coil of transformer be laminated?
Ans: When curent flows through the coil of transformer, eddy current is produced in the core. If the coil of transformer becomes a single piece, the amount of eddy current increases and the transformer gets heated and damaged. Output is also low. So, the coil of transformer is laminated.
Differentiate between:
a) Phase wire and Neutral wire
Ans: Following are the differentiate between on phase and neutral wire:
| Phase wire | Neutral wire |
|---|---|
| It is a red/ brown colored wire connected electrical device (load) to input current. | It is a black or blue colored wire through which current from load returns back. |
| We feel electric on touching it. | We feel electric on touching it. |
Numerical problems:
i. Power consumption (pc): Power (P) × Hour(H)
=Watt × Hours
= KWH
=Unit
ii. Watt = Volt × Amper
Power = Volt (V) × current (Amper)
According to ohm’s law:
V = IR
PD = Current × Resistance
Volt Amper ohm (Ω)
a) An electric kettle rated 220 V and 2.2 KW works for 3 hours. Find the energy consumption and current drawn by it.
Given data,
PD = 220 volt
Power= 2.2 kw
Time = 3 hours
We know that,
Power consumption= power × hour
= 2.2kw × 3 hour
=6.6 KWH
= 6.6 Unit
Again, current drawn (I)= ?
P=VI
∴ I = P/V = 2.2 × 100W/ 220 = 2200/220
=10 AMP
∴The energy consumption is 6.6 unit and current drawn by it is 10 AMP.
b) If a 1000W heater is to be operated at a 220V mains, what must be the rating of the force to be used in the circuit?
Given data,
P = 1000 W
PD= 220V
Fuse (I)= ?
We know that,
P =VI
∴I = P/V= 1000/220
=50/11 = 4.5 = 5AMP
∴So the 5AMP is the rating of the force to be used in the circuit.
c) If two irons of 750W each are used 8hours a month. How much tariff should be paid? Cost of one unit of electricity is Rs 7.
Given data,
P= 750W
T=2 month
N= 8 hours
We know that,
Power consumption= 750 × 8 × 2
= 2 × 750 × 8/ 1000
= 12 KHW
=2 unit
∴ The cost of 1 unit= Rs. 7.00
∴The cost of 12 unit = 12×7 = Rs. 84.00
d) What type of combination of cells is shown in the given circuit? Calculate the power of the bulb if 0.2Acurrent flows through the curcuit.
Given data,
Amp= 0.2
Volt = 6
We know that,
Watt= Volt × Amp
= 6×0.2
=1.2 watt
e) In a transformer, the number of turns in primary coil is 100. If the primary and secondary voltage are 220V and 110V respecctively, calculate the no of turns in the secondary coil.
Given data,
Np= 100
Vp= 220 volt
Vs= 110 volt
Ns=?
we know that,![]()
Question Light
Answer these following questions
- What is the lens? Mention its types.
Ans: The lens is the medium of refraction of light.
Its types are:
a) Convex lens
b) Cocave lens, etc. - Define the following:
a) Centre of curvature: The center of the sphere of which the lens part is called the center of curvature.b) Principal axis: An imaginary line which joins two centers of curvatures (C1 and C2) is called Principal axis.c) Optical center: The center of a lens which is equidistant from all points of its surface is called Optical center.d) Principal focus: Principal focus is a point on the principal axis where the rays of light parallel to the principal axis coverage after refraction through a convex lens or appear to diverge after refraction through a concave lens.e) Focal length: The distance between the optical center and the principal focus is called Focal length. - What is magnification? Mention the formula for finding the magnification of an object.
Ans: Magnification is a factor which determines image is how many times larger or smaller than an object.
The formula for finding the magnification of an object
Magnification (m)= size of image/size of an object
= Image distance (v)/ Object distance(0) - A convex lens forms a real and magnified image where is the object placed?
Ans: A convex lens forms a real and magnified image when it is the object placed between 2F and F. - What is the power of the lens? Mention its formula.
Ans: The conversing or diverging capacity of a lens is called Power of lens.
Power of lens (P)= 1/ focal length (m) - Mention the lens formula.
Ans: Power of lens (P)= 1/ focal length (m) - Mention the uses of the lens.
Ans: The uses of the lens are:
a) It is used in a camera.
b) It is used in remedy defect of eyesight, etc. - What are optical instruments?
Ans: The instruments which produce the image of an object are called optical instruments. - How does pupil control the amount of light entering the eyes?
Ans: Pupil controls the amount of light entering the eye by changing the size of a pupil by iris. - What is accommodation?
Ans: The ability of the eye to focus the image of an object on the retina by changing the focal length of its lens is called Accommodation. - What is Near point?
Ans: The nearest point up to which a normal eye can see clearly is called Near point. - Define Far point.
Ans: The farthest point up to which a normal eye can see clearly is called Far point. - What is Range of vision?
Ans: The distance between near point and far point is called Range of vision. - Define Defect of vision.
Ans: When an eye cannot see the object lying at the range of vision is called Defect of vision. - Ram cannot see the letter written on the blackboard. What is his defect of vision? How can it be corrected?
Ans: Ram cannot see the letter written on the blackboard because he is suffering from Myopia and he needs to wear goggles rear with the concave lens.
Give reasons:
- Shortsightedness can be removed by using the concave lens.
Ans: Shortsightedness can be removed by using the concave lens because it concentrates light coming from the distant object of near point (N). - A concave lens is called a diverging lens.
Ans: A concave lens is called a diverging lens because of it diverse parallel light from a point. - A convex lens is called a converging lens.
Ans: A convex lens is called a converging lens because it converses parallel light at a point (focus). - Power of a convex lens is positive.
Ans: Power of a convex lens is positive because the real distance between the optical center and the real image is taken as positive.
Numerical Problems
a) Find the power of a lens of focal length 10 cm.
Given data,
f= 10 cm
= 10/100 cm
we know that,
p=1/f(m)
=1/10/100
= 100/10
= 10 D
∴ Power of focal length is 10 D.
b) What is the focal length of a lens having the power 5D?
Given data,
p= 5D
f=?
we know that,
p=1/f(m)
f(m)= 1/p = 1/5 -= 0.2 m.
∴ The focal length of a lens is 0.2m.
c) An object is placed at a distance of 60cm in front of a convex lens of a focal length 20cm. where is the image formed? Mention magnification of the image and power of the lens.
Given data,
u=60cm
f=20cm
v=?
m=?
p=?
we know that,
1/f = 1/u + 1/v
1/20 = 1/60 + 1/v
1/20 + 1/60 = 1/v
3+1/60 = 1/v
or, 1/v= 4/60 =1/15
∴v= 15 cm
Now,
Magnification (m)= Image distance(v) / Object distance(u)
=15/60
=1/4
=0.25
Again, p=1/f(m)
=1/20
=1/20/100
=100/20
=5D
∴The magnification of the image is o.25 and power lens is 5D.
d) An object is placed at the distance of 40 cm from the concave lens of focal length 20cm. Find the image distance.
Given data,
u= -40
f= -20cm
we know that,
1/f= 1/u+1/v
1/-20= 1/-40 = 1/v
1-1/40= 1/v
-1/40= 1/v
-v=40
∴v= -40
∴The image distance is -40cm.
e) A student wears spectacles of power -2d. What types of defect of the eye does the student have? Find the focal length of the lens used?
Given data,
p=-2D
f=?
we know that,
p= 1/f(m)
or, -2= 1/f(m)
or, f(m)= 1/-2
∴f(m)= -50cm∴The focal length of the lens used is -50cm.
Energy Question Answer
- What is the primary and secondary source of energy?
Ans: The source of energy which can be used in the same form in which they present naturally are called the primary source of energy.
The source of energy which is obtained from the primary source is called the secondary source of energy. - What is renewable energy? Give some examples.
Ans: The source of energy which can be obtained again and again when one exhausted is called the Renewable source of energy.
Examples: Biogas, Nuclear fuel, etc. - What is the Nonrenewable source of energy? Give some examples.
Ans: The source of energy which can’t be obtained when exhausted is called the Non-Renewable source of energy.
Examples: Fossil fuel, Petrochemical, etc. - What is a fossil fuel? Give some examples.
Ans: The source of energy which can be obtained by dead decayed plants and animals of millions of years ago is called a fossil fuel.
Example: Coal, petrol, etc. - What is hydro-power? Mention its advantages.
Ans: The power produced by the power of water is called Hydropower.
Its advantages are:
a) It is pollution free.
b) It is a renewable source of energy.
c) It transforms from one form to another.
d) It operates on modern devices, etc. - What is the energy crisis? What is the various way to solve the problem of the energy crisis?
Ans: The problem created by the exhaustion of fossil fuel reserves due to excessive use is called energy crisis.
The various way to solve the problem of the energy crisis is given below:
a)By avoiding unnecessary use of electricity.
b)By conserving the existing source of energy.
c)By producing and using more hydro-electricity.
d)By developing the alternating source of energy, etc. - What is the alternate source of energy? What is the various alternate source of energy?
Ans: The substitute for non-renewable energy is called the Alternate source of energy. The alternate source of energy is the renewable source of energy.
The various source of alternate energy is given below:
a)Biogas,
b)Solar energy, etc. - What is Biogas? How is it obtained?
Ans: Biogas is produced from organic matter which can be used as an energy source. It can be obtained from animal dung. - What is the advantage of biogas?
Ans: The advantage of biogas are given below:
a)It doesn’t produce smoke.
b) It can be used for cooking food.
c) It is a renewable source of energy, etc. - What is nuclear fuel? What are the various types of nuclear reactions?
Ans: The elements which produce a large amount of energy as a result of nuclear reactions are nuclear fuels.
The various types of nuclear reactions are given below:
a)Nuclear fission
b)Nuclear fusion, etc. - Mention advantage of nuclear energy.
Ans: Advantage of nuclear energy are given below:
a) A small amount of nuclear energy produces a huge amount of energy.
b) It is used by few, so it can be alternate energy, etc. - What is wind energy? Mention its advantages.
Ans: The energy which contains wind at high speed is called wind energy.
Its advantages are:
a)It is free of cost.
b) It is a renewable source of energy.
c) It can be used to generate electricity.
d) It provides energy without depleting energy, etc. - What is geothermal energy? Mention its advantages.
Ans: The energy obtained by heat energy available inside the earth is called Geothermal Energy.
Its advantages are given below:
a) It supplies energy without pollution.
b) It is a perpetual source of energy.
c) It can generate electricity, etc. - What is solar energy? Write its uses?
Ans: The energy obtained from the sun is called Solar energy.
Its uses are:
a) For drying clothes.
b) For preserving fruits.
c) For providing heat and light to the earth.
d) For obtaining heat and light energy, etc. - What are the two natural processes of obtaining geothermal energy?
Ans: The two natural process of obtaining geothermal energy are given below:
a)Volcanic eruption.
b)Hot water spring, etc.
Give reasons:
- Wind energy is the outcome of solar energy.
Ans: Wind energy is the outcome of solar energy because the heat of the sun causes the air of one planet to be heated. The hot air being lighter rises up and a vacant place is created. The cooler air from other places moves towards such vacant with great speed. - Biofuel and fossil fuel is the outcome of solar energy.
Ans: Biofuel and fossil fuel is the outcome of solar energy because plants convert solar energy into chemical energy and store it in their body. The biomass of plants and animals are used as biofuel. When plants and animals of million years ago died and got buried under the soil, they were converted into fossils. - Hydroelectricity is the outcome of solar energy.
Ans: Hydroelectricity is the outcome of solar energy because Iceberg is melt due to the heat of solar energy then it follows in high that is used to produce electricity. - Mineral oil is a fossil fuel.
Ans: Mineral oil is a fossil fuel because mineral oil is formed from dead bodies buried millions of years ago. - Biogas is the best energy source in Nepal.
Ans: Biogas is the best energy source in Nepal because Nepal is based on agriculture, so dung produce from animals is used to produce biogas. - Production of hydroelectricity should be encouraged.
Ans: Production of hydroelectricity should be encouraged because the production cost of hydroelectricity is high at the beginning, after that it will be run for a long time and produces heat.
Sunday, May 16, 2021
Featured Post
Meiosis
Meiosis Cell Division Prophase-I occurs over a long duration and involves several complicated changes in meiotic cell division. It is import...
-
Electromagnetic Induction a ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION Electromagnetic Induction is defined as the production of emf i...
-
Alternating Current a Alternating Current The current or emf whose magnitude changes with time and direction reverses periodically is...