Subject: Opt-II Science Time: 2:15 hrs F.M.: 75
Candidates are required to write their answers according to the
instructions given.
Attempt all questions.
Group 'A'
1. Give short answer to the following questions. 16´1=16
a) What is gravitational
field intensity?
b) Define viscosity.
c) What is biogas plant?
d) State principle of
calorimetry.
e) Define magnification.
f) What are quantum
numbers?
g) Define
electronegativity.
h) Write name two compounds
having coordinate covalent bond.
i) State Markonikov’s
rule.
j) Where do we use
sluice method?
k) Egg is considered as
reference protein, why?.
l) Write the major
event in the Diakinesis phase of Meiosis cell division.
m) Define coprophagy.
n) State law of independent
assortment.
o) Write any two examples of
antibiotics.
p) Write the advantage of
using reflector telescope though it is bulky in structure.
Group 'B' [13´2=26]
2.
Is current scalar of vector quantity? Write with reason.
3.
Suggest two suitable alternative source of energy in rural area of
Nepal with reasons.
4.
How can you identify whether the given lens is convex or concave?
5.
Explain in brief the terminals of a transistor.
6.
Write any four characteristics of modern periodic table.
7.
Explain in short the structure of Sulphur
trioxide with diagram.
8.
Calculate pOH of aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide whose hydroxyl
ions concentration is 10-1 m/l.
9.
What is aquaregia? Write its reaction with gold.
10.
What is enzyme? Write its two characteristics.
11.
Draw floral diagram of rice with its floral formula.
12.
Show in chart how haemophilia is transferred to a son from his carrier
mother.
13.
Write any two control measures for controlling high blood pressure.
14.
Write two difference between radio carbon dating and uranium lead
dating technique.
Group'C' [6´3=18]
15. Define elastic limit. Explain
Hook’s law in brief.
16. A brass rod of 200 gm mass at
100oC is dropped into 1.2 kg of water at 30oC. The
final temperature is 35oC. Calculate the specific heat capacity
of brass.
17. Define normal solution.
Calculate the molarity of 40 gram H2SO4in 100 ml
solution.
18. Define following organic reaction with one example of each:
a.
Substitution reaction b. Elimination reaction
19. What type of division is Meiosis I? Write one major events in each sub
phases of Meiosis I.
20. What is endocrinology? Write
the effect of hypo and hyper secretion of following hormone:
a.
thyroxine b. insulin
21. Explain how planetarium forms the image of stars?
Group 'D' [4´4=16]
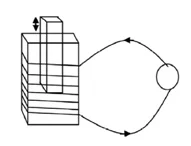
22.
Wind up an insulated copper wire in the match box as shown in the figure.
Connect two ends of the wire with a galvanometer and move a powerful bar
magnet in and out of a match box very quickly. According to this activity
answer the following questions.
a.
On which principle does the above activity work?
b.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is inserted
inside the match box?
c.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is taken out
from the match box?
d.
At which conditions the
needle of galvanometer comes in rest and deflects fast?
23. What do you mean by pH ? Explain in brief how following processes are
carried out:
i) Neutralization of the soil
ii) Treatment of hyperacidity
iii) Treatment of insect stings.
23. Draw a diagram to show nitrogen cycle and explain it in brief.
hög
SET II
Subject: Opt-II Science Time: 2:15 hrs F.M.: 75
Candidates are required to write their answers according to the
instructions given.
Attempt all questions.
Group 'A'
1. Give short answer to the following questions. 16´1=16
a) Define gravitational field
intensity.
b) Define elastic limit.
c) What do you mean by
briquette?
d) State principle of
calorimetry.
e) What is diode?
f) What are quantum
numbers?
g) Define normality.
h) State Aufbau
principle.
i) Write the basic
difference between coordinate bond and covalent bond.
j) Write one example of
addition reaction of organic compounds.
k) In which type of ores is
forth floatation process used for its concentration?
l) Define oligosaccharides.
m) Write the major event in the
Diakinesis phase of Meiosis cell division.
n) Define coprophagy.
n) Define nitrification.
o) Write any two examples of
antibiotics.
p) Which region of Nepal is
rich in brine water?
Group 'B' [13´2=26]
2.
Is current scalar of vector quantity? Write with reason.
3.
Obstruction of local is frequent in hydropower construction region.
Write any two reasons for it.
4.
How much heat is to be supplied in 40 gram of water at 300C
to increase its temperature to 400C?
5.
Magnification of a lens is -0.7. What does this mean?
6.
Calculate the pH of aqueous solution of nitric acid whose hydrogen ion
concentration is 10-3 m/l.
7.
Explain Saytjeff’s rule with an example.
8.
What is aquaregia? Write its reaction with gold
9.
Write any two industrial function of enzymes.
10.
Draw a chart to show F1generation when a hemophilia carrier
woman marries a normal man.
11.
Draw floral diagram of rice with its floral formula.
12.
How wetland benefits ecosystem? Write any two points.
13.
Write two major causes of hyperuricemia.
14.
Write two difference between radio carbon dating and uranium lead
dating technique.
Group'C' [6´3=18]
15. Define surface tension. Mention
two effect of surface tension what we see in our daily life.
16. Draw ray diagram of compound
microscope and explain in brief about its working.
17. State and explain Avogadro’s Law.
18. Explain the concept of ionic product of water.
19. Identify the followings and also write their one features:
a)
b)


20. Given table shows cross between
round and yellow seeded pea plant with wrinkled green seeded pea plant.
Answer the following questions:

i) Which generation is represented by the table?
ii)
Which law explains this? As write the law.
iii) What percentage of the offspring are round and yellow seeded pea
plant in this generation?
21. Explain how planetarium forms the image of stars?
Group 'D' [4´4=16]
22.Study the given figure and answer the following questions:
i) Which type of
generator is this?On the basis of which principle does it work upon?
ii) Draw a graph to show the nature of current produced.
iii)
a.
On which principle does the above activity work?
b.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is inserted
inside the match box?
c.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is taken out
from the match box?
d.
At which conditions the
needle of galvanometer comes in rest and deflects fast?
23. What do you mean by pH ? Explain in brief how following processes are
carried out:
i) Neutralization of the soil
ii) Treatment of hyperacidity
iii) Treatment of insect stings.
24. Draw a diagram to show nitrogen cycle and explain it in brief.
hög
SET III
Second Term Examination-2076
Class: - Ten
F.M.
- 45
Subject: - Opt. Science
Time:
- 1:30 Hrs
Group A (9×1=9)
1.
Write very short answer to the following questions:
a.
Define gravitational field intensity.
b.
What is surface tension?
c.
What do you mean by bio-mass energy?
d.
State principle of calorimetry.
e.
What do you mean by magnification?
f.
Define normal solution.
g.
State modern periodic law.
h.
What is Pi bond?
i.
Write one function of simple columnar epithelium.
Group B (8×2=16)
2.
Calculate the value of escape velocity on earth.
3.
Justify the statement " Iron is more elastic than rubber".
4.
Even though briquette is made from wood, why is it preferred than wood?
5.
Use of electric current would be limited if transformer was not
invented, why?
6.
What is azimuthal quantum number? Write the value of 'l' for n=2.
7.
Justify the position of potassium in modern periodic table with
suitable reasons.
8.
Calculate the pH of 10-2 molar solution of
H2SO4.
9.
Write any four characteristics of monocot stem.
Group C (4X3=12)
10. How can the concept of latent heat of fusion be determined
experimentally.
11.
Study the given diagram and answer the following questions.
i. Can this device work when it
is connected to a d.c. source? Why?
ii. What happens when the number of primary turns and
secondary
turns made equal?
iii. Calculate the number of turns in a secondary coil.
12.
Discuss in brief any three application of neutralization reaction.
13. Identity the given stages of cell division and write one
character of
each.
fig. i
fig ii
Group D (2×4=8)
14.
Explain the construction and working of a compound microscope.
15.
State and derive Avogadro's law. Calculate the volume of 5 mol of
nitrogen gas at STP.
***
SET V
First Term Examination
Class: -
Ten
F.M.
– 45 Subject:
- Opt. Science
Time:
- 1:30 Hrs
Group A (9×1=9)
1.
Answer the following questions:
a)
Define centre of gravity.
b)
What is surface tension?
c)
Define fluid pressure.
d)
What is a biogas plant?
e)
Define latent heat of fusion.
f)
State principle of calorimetry.
g)
Write one use of binocular.
h)
Define magnification of an optical instrument.
i)
What is semiconductor?
Group B (Very Short) (8×2=16)
2.
Write the differences between centrifugal force and centripetal
force.
3.
Write any two factors that affect viscosity of a liquid.
4.
Although solar panels are costly, it is the better option in some part
of the country. Justify.
5.
Draw a graph to show the change in temperature of water when heated
from 900C to 1100C on applying heat.
6.
Write an expression for heat equation and the meaning of the symbols
used.
7.
Why is a convex lens called conversing lens?
8.
Write any two characteristics of series combination of resistors.
9.
Why is transistor known as building block of all modern electronic
system?
Group C (Short Questions) (4 X 3=12)
10.
Derive an expression for the escape velocity.
11.
Write a paragraph on “Benefits of Briquettes”.
12.
Calculate the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 500
gram of ice at 400C into water vapour at 1000C.
(Latent heat of vaporization = 22.5 ×105 J/Kg).
13.
The figure given alongside is a diagram of PN junction diode. Answer
the following questions:
a) You have a circuit of a cell and a bulb. Add this device in the
circuit in such a way that the bulb will continue glowing.
b) N-type semiconductor is added at left side in the above device. What
is the name of device thus formed? Draw its circuit symbol.
Group D (Long Question Answer)(2×4=8)
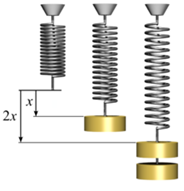
14.
Study the figure and answer the questions:
a. Write the observation of the experiment.
b. Which law is explained by the experiment? State the law.
c. What happens when a massive body is suspended in the spring? Writhe
with reason.
15.
You need to observe a minute pollen grain in details. What instrument
will you use? Draw a ray diagram to show its working. Also compare
between the two lenses used in the instrument.
***
SET VI
Third Term Examination
Class: - Ten
F.M.
- 75
Subject: - Opt. Science
Time: - 2:15
Hrs
Group A
1. Answer the following questions in very short.16×1=16
b.
Write down any two gases which are primarily present in biogas.
c.
State principle of calorimetry.
e.
What is electromagnetic induction?
f.
Write down the value of Avogadro's number.
g.
Define Ionization potential.
h.
What is the value of ionic product of water (Kw) at 25 degree
Celsius?
i.
What are nucleophiles?
j.
Write two chief ores of aluminum.
k.
Which two monosaccharide do lactose contain?
l.
Which enzyme converts protein into peptones?
m.
Write any two examples of sex linked diseases.
n.
What is biogeochemical cycle?
o.
Name the organ that cannot be transplanted till now.
p.
Write any two examples of fossils preserved in Natural History Museum
(NHM) of Nepal.
Group B
Answer the Following questions in short 13×2=26
2.
Write any two differences between centrifugal force and
centripetal force.
3.
A sewing needle placed carefully on the water floats even though its
density is higher than thedensity of water. Why?
4.
Latent heat of vaporization of water is 22.5 x 105joules
per kg. What does it mean?
5.
Distinguish between the nature of image formed by the eye lens and
objective lens of telescope.
6.
Write any two differences between sigma and pi bonds.
7.
How can we reduce hyperacidity? Describe in brief.
8.
Which rules govern the given reactions? State the rules too.
(i)
CH3-CH2-CH2
–CH2-CHBr–CH3 →
CH3-CH2-CH=CH-CH3
(ii)
CH3-CH=CH2 + HBr → CH3-CHBr-CH3
9.
Write down the balanced chemical reaction of gold with aquaregia.
10.
Why should athletes, labourers, etc. need high carbohydrate in their
diet?
11.
Compare monocot and dicot stem with any two points.
12.
"All hormones are chemical signals." Give reason.
13.
Write short note on biological nitrogen fixation.
14.
The average half-life of radioactive carbon
(6C14) is 5735 years. What does it mean?
Group C
Answer the Following
questions.
7×3 = 21
15.
The mass of the Earth is 6.0 × 1024 kg and its radius is 6.4
x 106m. Find the gravitational fieldintensity at a point on
its surface. What is the weight of a body of mass 100 kg on its surface?
(G= 6.67x 10-11 Nm2/kg2)
16.
How is biogas produced? Explain with diagram.
17.
Calculate the molecular mass of Ammonium carbonate and Calcium
Carbonate.
18.
Explain the formation of sodium chloride molecule with the help of
diagram.
19.
Draw the internal structure of monocot stem and label the parts
hypodermis and metaxylem.
20.
Explain the process of determining blood group with diagram.
21.
How planetarium is formed the images of the stars?
Group D
Answer the Following long questions. 3×4=12
22.
Wind up an insulated copper wire in the matchbox as shown in the
figure. Connect two ends of the wire with a galvanometer and move a
powerful bar magnet in and out of a match box very quickly. According
to this activity answer the following questions.
a.
On which principle does the above activity work?
b.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is inserted
inside the match box?
c.
What happens in the needle of galvanometer when the magnet is taken out
from the matchbox?
d.
At which conditions the needle of galvanometer comes in rest and
deflects fast?
23.
Hydrogen can be placed in group IA along with the alkali metals and
in group VIIA along with the halogens. Justify its position with two
points each.
24.
A homozygous plant having round seed and inflated pods is first
cross pollinate with a homozygous plant having wrinkled seed and
constricted pods and then self-pollinate. What result will be obtained
in second generation? Show your result up to F2 generation
indicating the phenotype and genotype ration in chart.
***